Explore the world of composite press with this insightful blog post. Discover the impact and significance of composite materials in the press industry. Uncover how composite press technology is revolutionizing manufacturing processes and enhancing product quality. Learn about the versatility and durability of composites, making them a preferred choice for various applications. Dive into the details of how composite press machines operate and their advantages over traditional methods. Stay tuned to grasp the future trends and innovations shaping the composite press sector.
Understanding Composite Press Basics
Definition
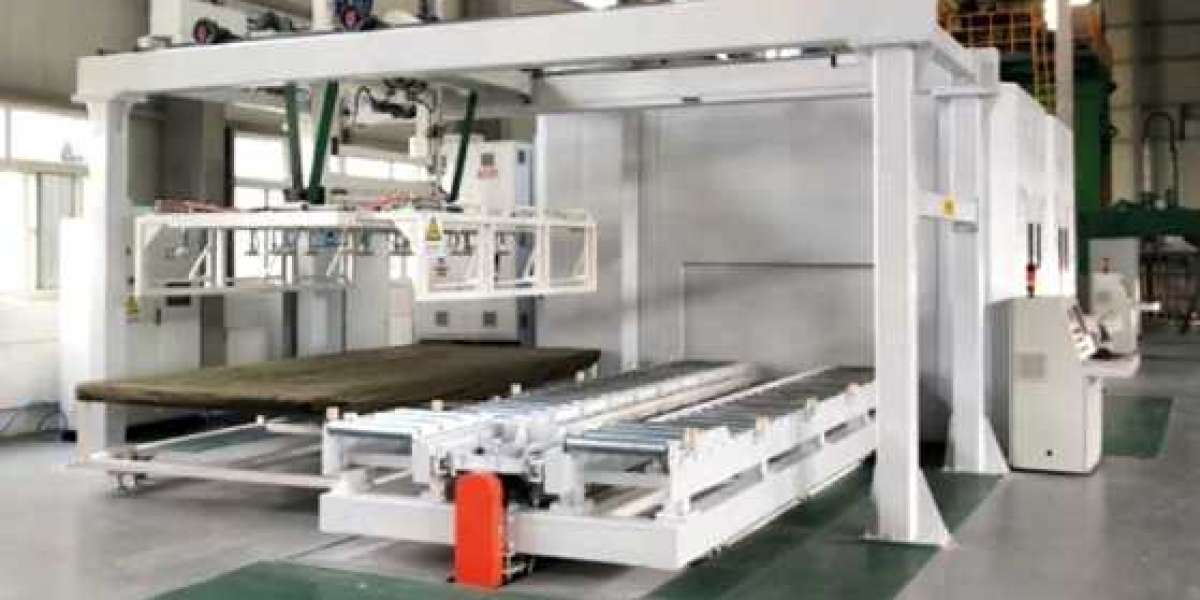
Composite press is a machine used in manufacturing to combine materials into a single structure. It plays a crucial role in creating strong and durable composite products.
Composite press machines exert pressure and heat to mold materials like fiberglass, carbon fiber, and resin into specific shapes.
Functions
The primary function of composite presses is to bond layers of materials together under high pressure. They ensure that the composite materials are evenly distributed and adhere properly.
These machines also help in shaping the final product by applying precise amounts of pressure and temperature during the curing process.
Key Manufacturers
Wabash MPI: Known for their hydraulic presses, Wabash MPI offers a wide range of composite press solutions for various industries.
French Oil Mill Machinery Company: Specializing in custom-engineered composite press systems, they cater to the unique needs of different manufacturing processes.
Dieffenbacher: A global leader in press systems, Dieffenbacher provides innovative solutions for composite material processing.
Key Components of Composite Presses
Structures
Composite presses typically consist of a heating system to cure the composite parts, a mold cavity where the materials are formed, and a hydraulic system for applying pressure.
Types
There are various types of composite presses, including hot presses, which use heat to cure materials, and cold presses, which rely on ambient temperature curing processes.
Composite presses can also be categorized based on their pressing method, such as mechanical presses that use mechanical force or hydraulic presses that utilize hydraulic power.
Role of the Ram
The ram in a composite press plays a crucial role in applying pressure to the composite materials within the mold cavity. It ensures proper consolidation and curing of the parts.
The ram's movement is controlled by the press's hydraulic system, allowing for precise application of pressure to achieve the desired quality and strength in the final composite parts.

How Composite Presses Operate
Hydraulic Mode
Composite presses in hydraulic mode utilize fluid pressure to generate force for molding materials. The hydraulic system comprises a pump, valves, and cylinders that apply pressure uniformly.
Hydraulic composite presses offer consistent pressure control, ensuring precise molding of composite materials. They excel in applications requiring high force and compression.
Electric Mode
Electric composite presses function using electrically driven components such as motors and servomechanisms. These presses provide rapid response times due to the direct conversion of electrical energy into mechanical force.
Electric composite presses are known for their energy efficiency and low maintenance requirements compared to hydraulic counterparts.
Mechanical Mode
In mechanical mode, composite presses operate through mechanical linkages like gears, cams, and levers. These presses rely on mechanical advantage to exert force on the material being molded.
Mechanical composite presses are favored for their simplicity and durability, making them suitable for applications where high precision is not critical.
Force Generation in Press Mechanisms
Contact Force
Press mechanisms generate force through the application of contact force. This force is essential for pressing materials together during the manufacturing process.
Contact force is created by the press's heated platens, which come into contact with the materials being pressed. The pressure applied by these platens results in the generation of force within the press mechanism.
Stroke Length
Another critical factor in force generation is the stroke length of the press. The distance over which the platens move to apply pressure directly impacts the amount of force exerted on the materials.
By adjusting the stroke length, manufacturers can control the level of force applied during the pressing operation. This customization ensures that different types of composite materials are pressed with optimal force for their specific requirements.
Importance of Force Generation
The proper generation of force in press mechanisms is crucial for achieving high-quality composite products. Insufficient force can result in incomplete bonding between materials, leading to weak spots or delamination.
On the other hand, excessive force can damage delicate materials or cause them to deform unnaturally. Therefore, maintaining an optimal level of force through precise control is vital for ensuring product integrity and performance.
Relationship with Composite Press Functions
The relationship between force generation and the functions of composite presses is symbiotic. The ability to generate adequate force directly influences the efficiency and effectiveness of a press machine.
Composite presses rely on controlled force to consolidate layers of materials, remove air pockets, and ensure uniform distribution throughout the product. Without proper force generation, these essential functions cannot be performed accurately, compromising the quality of the final composite product.
Control Systems of Composite Presses
Automatic Control
Composite presses utilize various control systems for efficient operation. One common type is the automatic control system, which regulates processes without manual intervention. These systems are programmed to adjust parameters like pressure and temperature automatically.
PLC-Controlled Systems
Another prevalent control system in composite presses is the PLC-controlled system. Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) offer versatility in programming and monitoring press operations. They ensure precise control over variables such as heating, cooling, and pressure.
CNC Systems
Composite presses often employ CNC systems for advanced control capabilities. Computer Numerical Control (CNC) technology enables intricate control of press functions, enhancing precision and repeatability in manufacturing processes.
Hand-Operated Controls
In contrast to automated systems, some composite presses feature hand-operated controls. While less common in modern industrial settings, hand-operated controls provide a more hands-on approach to adjusting press parameters.
Control systems play a crucial role in optimizing the performance of composite presses. By regulating variables such as temperature, pressure, and cycle times, these systems ensure consistent product quality and operational efficiency.
Using automatic control systems offers several advantages in composite press operations. Firstly, automatic systems reduce the risk of human error by maintaining precise control over critical parameters. Secondly, they enhance productivity by streamlining processes and minimizing downtime associated with manual adjustments.
Advantages of Automatic Control Systems:
Improved precision in parameter adjustment
Enhanced operational efficiency through automation

Characteristics and Specifications
Precision Parts
Composite presses are designed to handle precision parts with utmost accuracy, ensuring consistent quality in the final products. The precision offered by these presses is crucial for industries requiring high-quality components.
Materials and Construction
Utilizing a wide range of materials such as carbon fiber, these presses are built to withstand varying temperatures and pressures during production. The robust construction ensures durability and longevity in operation.
Customization Options
One of the key features of composite presses is the ability to customize various parts according to specific requirements. This flexibility allows manufacturers to adapt the press for different projects easily.
Maintenance and Cost Efficiency
Composite presses are known for their relatively low maintenance requirements compared to other types of presses. This factor contributes to cost efficiency in the long run, making them an attractive investment for businesses.
Standard Compliance
These presses adhere to strict industry standards, ensuring that the produced components meet required specifications consistently. Manufacturers can rely on composite presses to deliver quality outputs that meet regulatory requirements.
Technical Specifications
When selecting a composite press, factors such as temperature, pressure capacity, frame design, and tooling options play a crucial role. Understanding these technical specifications is essential for choosing the right press for specific production needs.
Contact Time Efficiency
Composite presses offer quick contact times, allowing for efficient production processes. The reduced contact time enhances productivity levels, making them ideal for high-volume manufacturing environments.
Size Variants
From small-scale models suitable for laboratory settings to large industrial-grade machines, composite presses come in various mm sizes. This versatility caters to different production scales and requirements.
Applications in Various Industries
Automotive Sector
Composite presses play a crucial role in the automotive industry, where they are used to manufacture lightweight and durable components. These presses help in producing parts such as car body panels, interior components, and structural reinforcements.
The automotive sector benefits significantly from the use of composite presses due to their ability to create strong yet lightweight materials. This results in improved fuel efficiency, better performance, and enhanced safety features in vehicles.
Aerospace Industry
In the aerospace sector, composite presses are widely utilized for manufacturing aircraft components like wings, fuselage sections, and interior structures. These presses enable the production of high-strength materials essential for ensuring aircraft durability and performance.
The aerospace industry relies on composite presses to reduce the overall weight of aircraft while maintaining structural integrity. This leads to increased fuel efficiency, lower operational costs, and improved aerodynamics.
Renewable Energy Sector
Renewable energy industries such as wind power generation benefit from composite presses for producing turbine blades. These presses are instrumental in creating large and sturdy blades that can withstand harsh environmental conditions.
The renewable energy sector leverages composite presses to enhance the efficiency and durability of wind turbines. By using these advanced manufacturing processes, companies can increase energy output while reducing maintenance requirements.
Marine Engineering
In marine engineering, composite presses are essential for fabricating boat hulls, decks, and other marine components. The use of these presses results in lightweight yet robust structures that offer excellent corrosion resistance in marine environments.
Marine engineering applications benefit from composite presses by improving vessel performance, longevity, and overall sustainability. The use of composite materials ensures that marine structures remain durable and efficient over extended periods.
Benefits of Composite Presses
Lightweight materials improve fuel efficiency.
Enhanced durability leads to longer product lifespan.
High strength-to-weight ratio ensures structural integrity.
Corrosion resistance increases component longevity.
Versatile manufacturing process allows for complex shapes and designs.
Closing Thoughts
The exploration of composite presses has shed light on their fundamental components, operational mechanisms, force generation aspects, control systems, specifications, and diverse industrial applications. Understanding these elements is crucial for grasping the intricate workings and versatility of composite press technology. The comprehensive overview provided in the preceding sections serves as a foundation for appreciating the significance of composite presses in modern manufacturing processes.
For those involved in the industrial sector, further research into advanced composite press technologies and their evolving applications is recommended. Delving deeper into this subject can unlock innovative solutions, streamline production processes, and enhance overall efficiency. By staying informed about the latest developments in composite press technology, individuals and industries can harness its full potential for driving progress and achieving manufacturing excellence.

Frequently Asked Questions
What are the key components of composite presses?
Composite presses typically consist of a hydraulic system, press frame, heating system, and mold. These components work together to apply pressure and heat to composite materials for molding or forming processes.
How do composite presses operate?
Composite presses use hydraulic systems to apply pressure on composite materials placed between molds. The press frame closes, pressure is applied, and heat may be used to cure the material. This process helps in shaping or molding the composites into desired forms.
What is force generation in press mechanisms?
Force generation in press mechanisms refers to the ability of composite presses to exert pressure on materials during the molding process. Hydraulic systems generate force through pistons, which push against the material with controlled intensity for shaping or forming purposes.
What are the control systems of composite presses?
Control systems in composite presses include PLCs (Programmable Logic Controllers) and HMI (Human-Machine Interface) panels. These systems regulate parameters such as temperature, pressure, and timing during the pressing operation, ensuring precise control over the molding process.
In what industries are composite presses commonly used?
Composite presses find applications across various industries like aerospace, automotive, marine, and construction. They are utilized for manufacturing components such as aircraft parts, automotive body panels, boat hulls, and structural elements due to their ability to efficiently shape composite materials.