In the rapidly evolving landscape of the Internet of Things (IoT), low-power antennas are emerging as a pivotal technology. These antennas are designed to operate efficiently while consuming minimal energy, making them ideal for a wide range of applications, from smart homes to industrial automation.
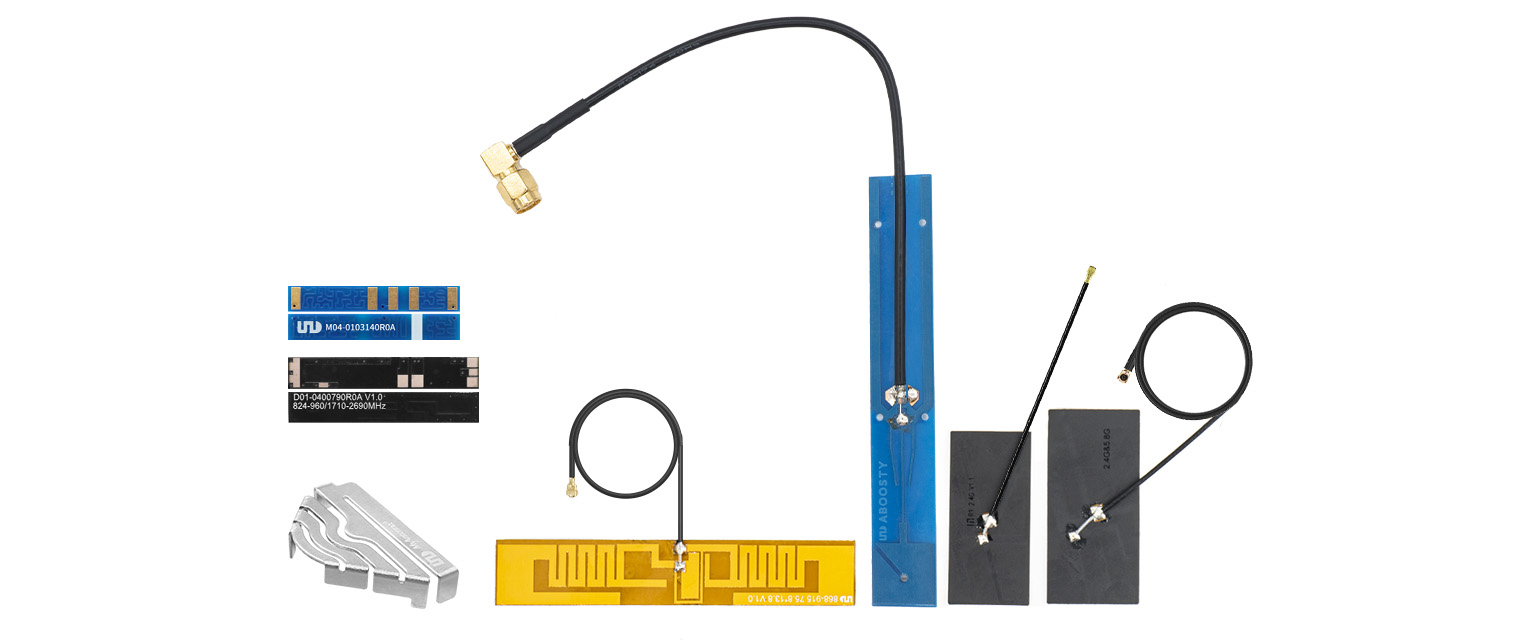
Understanding Low-Power Antennas
Low-power antennas are specifically engineered to transmit and receive signals with reduced energy consumption. This characteristic is crucial for devices that rely on battery power, as it extends their operational lifespan. But what exactly makes these antennas so effective?
- They utilize advanced materials and designs to minimize energy loss.
- They often operate on lower frequencies, which can enhance signal penetration and range.
- They are compatible with various communication protocols, including LoRa, Zigbee, and NB-IoT.
Benefits of Low-Power Antennas in IoT
The integration of low-power antennas into IoT devices offers numerous advantages:
- Energy Efficiency: By consuming less power, these antennas help in reducing the overall energy footprint of IoT systems.
- Extended Range: Low-power antennas can maintain connectivity over longer distances, which is essential for applications like smart agriculture and remote monitoring.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Reduced energy consumption translates to lower operational costs, making IoT solutions more economically viable.
- Enhanced Reliability: These antennas can provide stable connections even in challenging environments, ensuring consistent data transmission.
Applications of Low-Power Antennas
Low-power antennas are versatile and can be applied in various sectors:
- Smart Cities: They facilitate efficient traffic management and environmental monitoring.
- Healthcare: Wearable devices equipped with low-power antennas can continuously monitor patient health without frequent recharging.
- Agriculture: Sensors in fields can transmit data about soil conditions and crop health, optimizing resource use.
Future Prospects
As the demand for IoT devices continues to grow, the role of low-power antennas will become increasingly significant. Innovations in antenna technology are expected to enhance their performance further, making them even more integral to future connectivity solutions.
For more insights into the advancements in embedded antennas and their impact on IoT connectivity, visit  .
.
In conclusion, low-power antennas are not just a trend; they represent a fundamental shift in how we approach connectivity in the IoT landscape. By prioritizing energy efficiency and reliability, these antennas are paving the way for a more connected and sustainable future.