Global Positioning System (GPS) antennas have undergone significant transformations since their inception. These devices are crucial for accurate location tracking and navigation. Understanding the evolution of GPS antennas provides insight into how they have become integral to various applications, from personal navigation devices to advanced military systems.
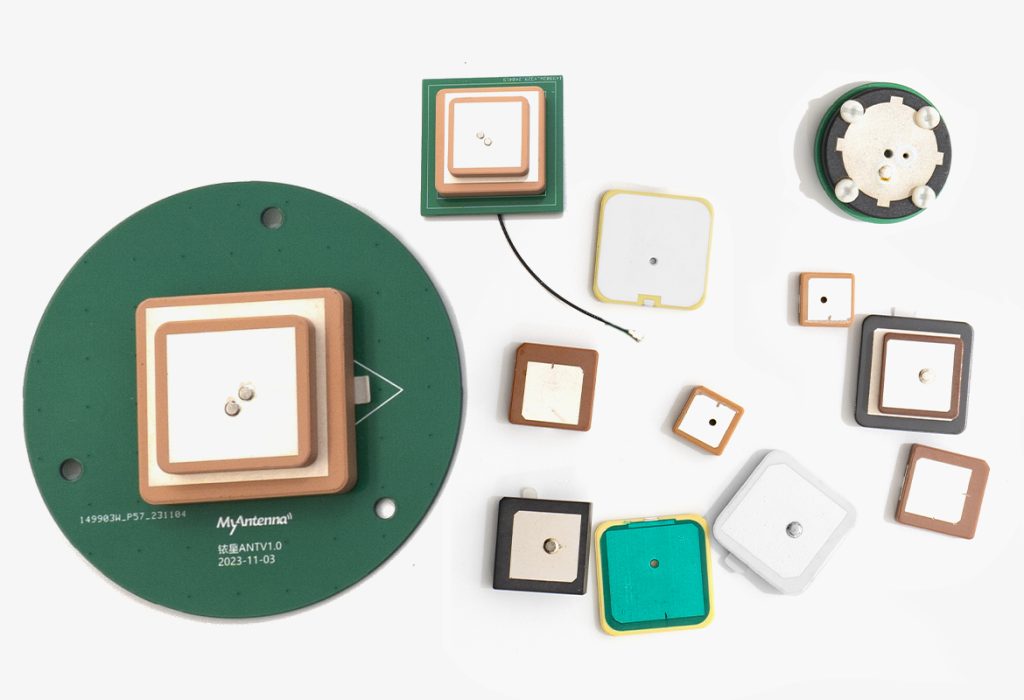

Understanding GPS Antennas
At their core, GPS antennas are designed to receive signals from satellites orbiting the Earth. These signals are then processed to determine precise locations. But what makes a GPS antenna effective? The answer lies in its design and technology. Various types of antennas, such as patch, helical, and dipole antennas, serve different purposes and environments.
Types of GPS Antennas
- Patch Antennas: These are compact and widely used in consumer electronics.
- Helical Antennas: Known for their high gain and circular polarization, ideal for mobile applications.
- Dipole Antennas: Simple and effective, often used in fixed installations.
Each type of GPS antenna has its unique advantages and is selected based on specific requirements such as size, gain, and application environment.
Technological Advancements in GPS Antennas
Over the years, advancements in technology have significantly enhanced the performance of GPS antennas. Modern antennas now incorporate sophisticated materials and designs that improve signal reception and reduce interference. For instance, the introduction of multi-band antennas allows devices to connect to multiple satellite systems, enhancing accuracy and reliability.
Key Features of Modern GPS Antennas
- Multi-frequency Support: This feature enables antennas to receive signals from various satellite constellations, such as GPS, GLONASS, and Galileo.
- Improved Sensitivity: Enhanced sensitivity allows for better performance in challenging environments, such as urban canyons.
- Compact Design: Modern designs are often smaller and lighter, making them suitable for portable devices.
These advancements not only improve the accuracy of location data but also expand the potential applications of GPS antennas in sectors like automotive, aviation, and even agriculture.
The Future of GPS Antennas
As technology continues to evolve, the future of GPS antennas looks promising. Innovations in materials science and signal processing are paving the way for even more efficient designs. Will we see antennas that can operate in more challenging environments or integrate seamlessly with other technologies? The possibilities are endless.
For those interested in exploring a wide range of GPS antennas, consider visiting  . This collection showcases various antennas tailored for different applications, ensuring you find the right solution for your needs.
. This collection showcases various antennas tailored for different applications, ensuring you find the right solution for your needs.
Conclusion
The evolution of GPS antennas reflects the broader advancements in technology and our increasing reliance on accurate navigation systems. From basic designs to sophisticated technologies, these antennas play a pivotal role in our daily lives. As we look to the future, the potential for further innovation remains vast, promising even greater accuracy and functionality in the world of GPS.