In the realm of wireless communication, magnetic antennas play a pivotal role. These antennas are designed to operate efficiently in various applications, from mobile devices to advanced communication systems. But how do they work, and what makes them so essential in today's technology landscape?
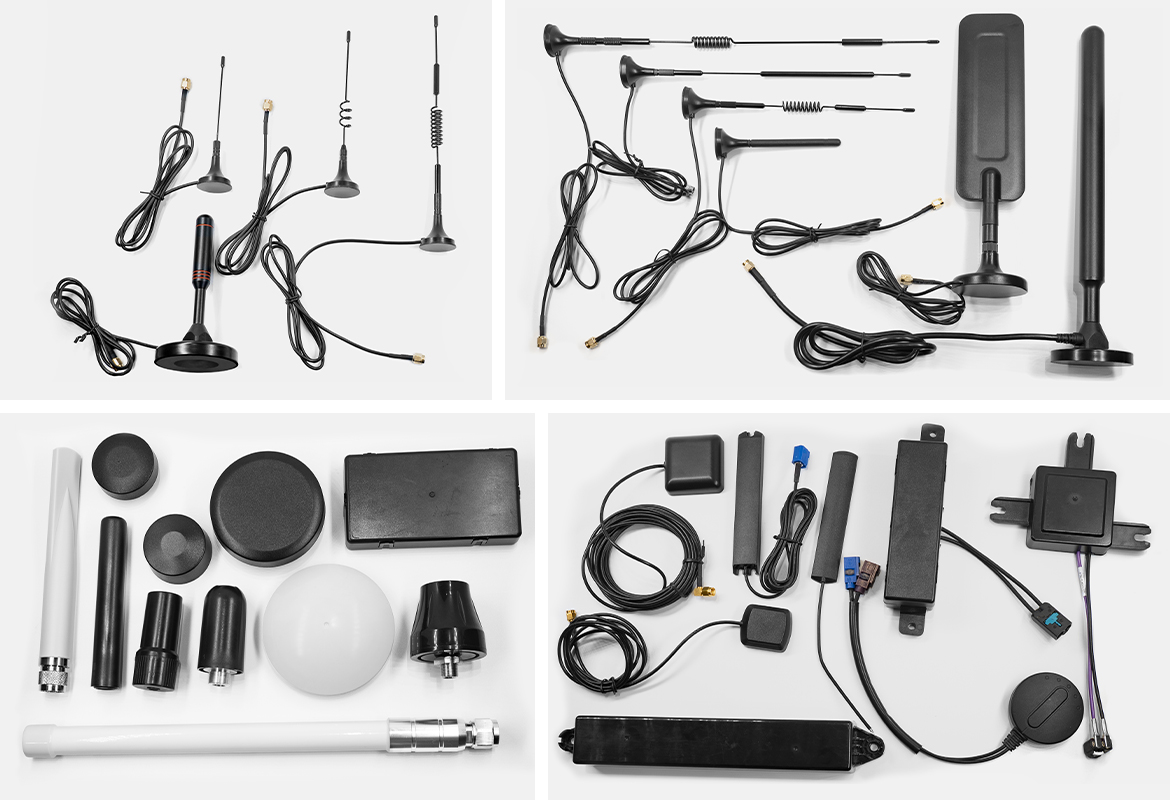

What Are Magnetic Antennas?
Magnetic antennas are specialized devices that utilize magnetic fields to transmit and receive electromagnetic waves. Unlike traditional antennas that rely on electric fields, magnetic antennas primarily depend on the magnetic component of the electromagnetic wave. This unique characteristic allows them to achieve high performance in specific frequency ranges.
How Do Magnetic Antennas Work?
The operation of magnetic antennas is based on the principles of electromagnetism. When an alternating current flows through the antenna, it generates a magnetic field. This magnetic field interacts with the surrounding environment, allowing the antenna to radiate or receive signals. The efficiency of this process is influenced by several factors, including:
- Frequency: Magnetic antennas are particularly effective at lower frequencies.
- Design: The physical structure and materials used in the antenna can significantly impact performance.
- Environment: The surrounding medium can affect the propagation of electromagnetic waves.
Applications of Magnetic Antennas
Magnetic antennas find applications across various fields. Some notable uses include:
- Mobile Communication: They enhance signal reception in smartphones and tablets.
- IoT Devices: Magnetic antennas are crucial for the connectivity of Internet of Things (IoT) devices.
- Satellite Communication: Their ability to operate effectively in challenging environments makes them suitable for satellite systems.
- RFID Systems: Magnetic antennas are integral to Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) technology, facilitating seamless data transfer.
Advantages of Using Magnetic Antennas
There are several advantages to employing magnetic antennas in various applications:
- Compact Size: They can be designed to be smaller and more lightweight than traditional antennas.
- Enhanced Performance: Magnetic antennas often provide better signal quality and range.
- Versatility: Their design allows for use in a wide range of frequencies and applications.
Conclusion
In summary, magnetic antennas are a vital component of modern communication technology. Their unique operating principles and diverse applications make them indispensable in various fields. For those interested in exploring high-quality magnetic antennas, consider visiting  for a comprehensive selection.
for a comprehensive selection.